C Programming Read From Keyboard Into Array
In simple English, an array is a collection.
In C also, it is a collection of like type of data which can be either of int, float, double, char (Cord), etc. All the data types must be same. For instance, we tin't accept an array in which some of the information are integer and some are float.

Why Array?
Suppose we need to store marks of 50 students in a form and calculate the average marks. Then, declaring 50 separate variables will practice the job simply no programmer would like to practise so. And there comes array in activeness.
How to declare an array
datatype array_name [ array_size ] ;
For example, accept an array of integers 'northward'.
int n[half dozen];
n[ ] is used to announce an assortment 'northward'. It means that 'n' is an array.
So, int n[vi] means that 'north' is an array of 6 integers. Here, 6 is the size of the array i.east. there are 6 elements in the array 'north'.
We demand to give the size of the array because the complier needs to allocate infinite in the retentivity which is not possible without knowing the size. Compiler determines the size required for an array with the help of the number of elements of an assortment and the size of the data type present in the assortment.
Here 'int n[half-dozen]' will classify infinite to 6 integers.
We tin can also declare an array by another method.
int due north[ ] = {2, 3, 15, 8, 48, 13};
In this case, we are declaring and assigning values to the assortment at the same time. Hither, there is no demand to specify the assortment size because compiler gets it from { 2,three,15,8,48,13 }.
Index of an Array
Every chemical element of an array has its alphabetize. Nosotros admission whatsoever element of an array using its index.
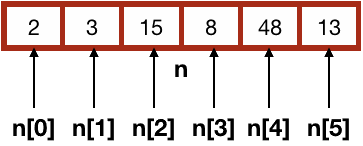
Pictorial view of the above mentioned assortment is:
0, 1, 2, 3, iv and 5 are indices. Information technology is like they are identity of 6 dissimilar elements of an array. Index always starts from 0. And so, the offset element of an assortment has a index of 0.
Index of an assortment starts with 0.
Nosotros admission any chemical element of an array using its alphabetize and the syntax to practice and so is:
array_name[index]
For example, if the name of an assortment is 'north', so to access the first element (which is at 0 index), nosotros write n[0].
Here,
due north[0] is ii
northward[1] is 3
north[ii] is 15
northward[3] is 8
northward[iv] is 48
due north[5] is 13
northward[0], northward[one], etc. are similar any other variables we were using till now i.e., we can set there value every bit due north[0] = 5; like we do with any other variables (x = 5;, y = 6;, etc.).
Assigning Values to Array
Past writing int n[ ]={ 2,4,8 }; , we are declaring and assigning values to the assortment at the same fourth dimension, thus initializing it.
Only when we declare an array like int n[iii];, we need to assign values to it separately. Considering 'int north[3];' volition definitely allocate infinite of iii integers in memory only in that location are no integers in that space.
To initialize information technology, assign a value to each of the elements of the array.
n[0] = 2;
n[1] = 4;
n[2] = viii;
It is only like we are declaring some variables and so assigning values to them.
int x,y,z;
x=two;
y=4;
z=8;
Thus, the first mode of assigning values to the elements of an array is past doing so at the time of its declaration.
int n[ ]={ 2,4,8 };
And the 2nd method is declaring the array kickoff and and then assigning values to its elements.
int n[iii];
due north[0] = 2;
northward[1] = 4;
n[2] = viii;
You tin understand this by treating northward[0], n[one] and n[2] equally similar to dissimilar variables you used earlier.
Just like variable, array can be of whatever other data type also.
float f[ ]= { 1.1, 1.4, 1.5};
Hither, 'f' is an array of floats.
First, permit's run into the instance to calculate the boilerplate of the marks of 3 students. Here, marks[0] represents the marks of the start student, marks[1] represents marks of the 2nd and marks[2] represents marks of the third educatee.
#include <stdio.h> int main () { int marks [ 3 ]; bladder boilerplate ; printf ( "Enter marks of outset student \n " ); scanf ( " %d" , & marks [ 0 ]); printf ( "Enter marks of 2d educatee \n " ); scanf ( " %d" , & marks [ 1 ]); printf ( "Enter marks of tertiary student \n " ); scanf ( " %d" , & marks [ 2 ]); average = ( marks [ 0 ] + marks [ 1 ] + marks [ 2 ]) / iii.0 ; printf ( "Boilerplate marks : %f \northward " , average ); render 0 ; }
Enter marks of kickoff pupil
23
Enter marks of second student
25
Enter marks of 3rd student
30
Boilerplate marks : 26.000000
Hither you just saw a working example of array, we treated elements of the array in an exactly like way as we had treated normal variables. &marks[0], &marks[ane] and &marks[2] represent the addresses of marks[0], marks[1] and marks[two] respectively.
In the in a higher place instance, two points should be kept in mind.
The boilerplate value should be of type 'float' because the average of integers can be bladder too.
Secondly, while taking out the boilerplate, the sum of the numbers should be divided by iii.0 and not 3, otherwise you lot will get the average value as an integer and non float.
We tin also use for loop every bit done in the adjacent example.
#include <stdio.h> int main () { int n [ 10 ]; /* declaring northward equally an array of x integers */ int i , j ; /* initializing elements of assortment northward */ for ( i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i ++ ) { printf ( "Enter value of n[%d]" , i ); scanf ( "%d" , & northward [ i ]); } /* printing the values of elements of assortment */ for ( j = 0 ; j < 10 ; j ++ ) { printf ( "north[%d] = %d \n " , j , due north [ j ]); } return 0 ; }
Enter value of north[0]12
Enter value of n[ane]34
Enter value of n[2]23
Enter value of north[3]78
Enter value of north[iv]32
Enter value of n[5]21
Enter value of n[6]4
Enter value of northward[7]23
Enter value of due north[8]46
Enter value of n[9]24
n[0] = 12
n[1] = 34
north[2] = 23
north[3] = 78
n[4] = 32
n[5] = 21
n[6] = 4
north[7] = 23
due north[viii] = 46
n[ix] = 24
The above code was just to brand yous familiar with using loops with an array because you volition be doing this many times later.
The lawmaking is elementary, 'i' and 'j' first from 0 considering the index of an assortment starts from 0 and goes up to 9 (for 10 elements). So, 'i' and 'j' goes up to 9 and not ten ( i<10 and j<ten ). And so, in the code n[i] will be n[1], northward[2], ...., north[9] and things will go accordingly.
If nosotros take declared an array with some array size and assigned values to simply some elements of that array, then the values of other elements are automatically assigned zero.
Suppose we declare and initialize an array as
int n[5] = { 12, 13, 5 };
This means that north[0]=12, n[i]=xiii and northward[two]=5 and rest all elements are zero i.due east. n[iii]=0 and due north[4]=0.
Similarly,
int n[5];
n[0] = 12;
n[1] = 13;
n[2] = 5;
In the above code, northward[0], north[1] and northward[2] are initialized to 12, 13 and five respectively. Therefore, n[4] and n[five] are both 0.
Array allocates face-to-face memory. Thus if the accost of the get-go element of an assortment of integers is 223698688 then the address of the 2nd element will be 223698692( 223698688+4 (4 is the size of one integer) ) and third will exist 223698696 so on. This means that the memories of all elements of an array are allocated together and are continuous.
Pointer to Arrays
Till now, we have seen how to declare and initialize an assortment. Now, we volition see how we tin have pointers to arrays too. But before starting, we are assuming that you accept gone through Pointers from the topic Point Me. If not, then first read the topic Pointers and exercise some bug from the Practise section.
As nosotros all know that pointer is a variable whose value is the address of some other variable i.e., if a variable 'y' points to some other variable 'x', it ways that the value of the variable 'y' is the address of '10'.
Similarly, if we say that a variable 'y' points to an array 'n', it would hateful that the value of 'y' is the address of the first element of the array i.due east. due north[0]. It means that the pointer of an array is the pointer of its starting time element.
The proper name of an array is the arrow to the first element of the array.
If 'p' is a arrow to array 'age', means that p (or age) points to age[0].
int age[50];
int *p;
p = historic period;
The above code assigns 'p' the accost of the showtime chemical element of the array 'historic period'.

Now, since 'p' points to the first chemical element of assortment 'age', '*p' is the value of the first element of the array.
Since *p refers to the offset assortment chemical element, *(p+1) and *(p+2) refers to the second and third elements respectively and so on.
And then, *p is age[0], *(p+ane) is age[1], *(p+2) is age[two].
Similarly, *historic period is age[0] (value at historic period), *(historic period+1) is age[1] (value at age+one), *(age+2) is age[2] (value at historic period+two) and and so on.
That's all in arrow to arrays.
At present let'southward see some examples.
#include <stdio.h> int main () { bladder due north [ v ] = { 20.four , xxx.0 , 5.viii , 67 , 15.two }; /* declaring north as an assortment of 5 floats */ float * p ; /* p as a arrow to bladder */ int i ; p = northward ; /* p at present points to array n */ /* printing the values of elements of array */ for ( i = 0 ; i < five ; i ++ ) { printf ( "*(p + %d) = %f \n " , i , * ( p + i ) ); /* *(p+i) ways value at (p+0),(p+ane)...*/ } return 0 ; }
*(p + 0) = 20.400000
*(p + 1) = thirty.000000
*(p + ii) = 5.800000
*(p + 3) = 67.000000
*(p + 4) = xv.200000
Every bit 'p' is pointing to the offset chemical element of array, so, *p or *(p+0) represents the value at p[0] or the value at the commencement element of 'p'. Similarly, *(p+1) represents value at p[1]. And *(p+3) and *(p+4) represents p[3] and p[4] respectively. So appropriately, things were printed.
The above example sums up the above concepts. Now, allow's print the address of the assortment and also individual elements of the array.
#include <stdio.h> int main () { int northward [ iv ] = { 20 , 30 , v , 67 }; /* declaring north as an array of 4 integers */ int * p ; /*a pointer*/ int i ; p = n ; /*p is pointing to array n*/ /* press the address of array */ printf ( "Accost of assortment n[4] = %u \northward " , p ); /*p points to array means store the address of the first element of assortment*/ /* printing the addresses of elements of array */ for ( i = 0 ; i < iv ; i ++ ) { printf ( "Address of n[%d] = %u \northward " , i , & n [ i ] ); } return 0 ; }
Accost of assortment n[four] = 2491554384
Accost of n[0] = 2491554384
Address of n[1] = 2491554388
Accost of n[2] = 2491554392
Accost of n[3] = 2491554396
As you have noticed that the accost of the showtime element of n and p are aforementioned and this means I was non lying!
You can impress other elements' addresses by using (p+i), (p+2) and (p+three) too.
Allow'due south laissez passer whole Array in Part
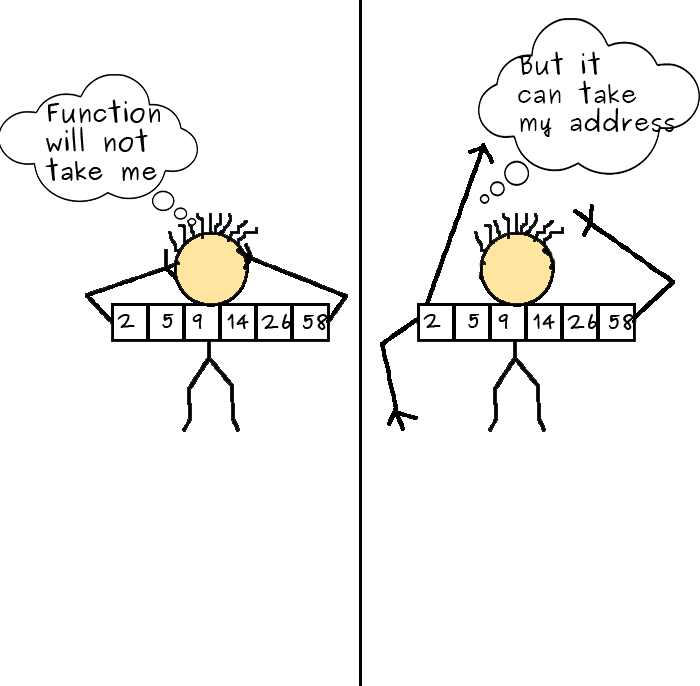
In C, nosotros tin pass an element of an array or the full array as an argument to a function.
Let's kickoff pass a single array element to function.
#include <stdio.h> void display ( int a ) { printf ( "%d \n " , a ); } int main () { int n [ ] = { 20 , 30 , 23 , four , 5 , 2 , 41 , viii }; display ( n [ 2 ]); return 0 ; }
Passing an entire Array in a Function
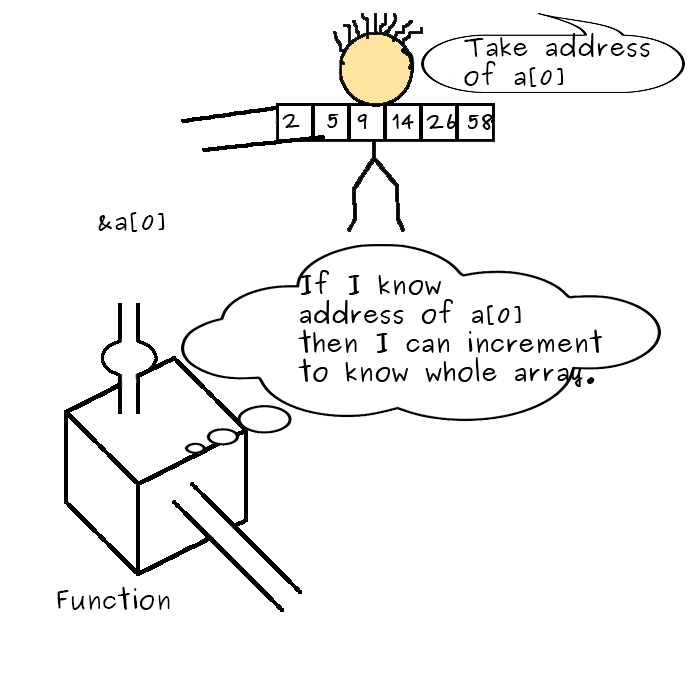
Nosotros tin too laissez passer the entire array to a function past passing array proper noun equally the argument. Yes, the fob is that nosotros volition pass the address of an array, that is the address of the beginning element of the assortment. Thus by having the pointer of the first element, we can get the entire array as nosotros have washed in examples above.
Permit's see an example to understand it.
#include <stdio.h> float average ( float a []) { int i ; float avg , sum = 0 ; for ( i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++ i ) { sum += a [ i ]; } avg = sum / 8 ; return avg ; } int main () { float b , n [ ] = { 20.6 , 30.8 , 5.1 , 67.two , 23 , 2.9 , 4 , viii }; b = average ( northward ); printf ( "Average of numbers=%.2f \northward " , b ); render 0 ; }
average(bladder a[]) → Information technology is the part that is taking an assortment of float. And rest of the torso of the function is performing accordingly.
b = average(n) → One affair yous should annotation here is that we passed 'n'. And as discussed earlier, 'n' is the pointer to the first chemical element or pointer to the assortment n[]. So, we have actually passed the pointer.
In the above example in which we calculated the average of the values of the elements of an array, we already knew the size of the array i.e. 8.
Suppose nosotros are taking the size of the array from the user. In that example, the size of the array is not fixed. Here, we need to pass the size of array as the second argument to the role.
#include <stdio.h> float average ( float a [], int size ) { int i ; float avg , sum = 0 ; for ( i = 0 ; i < size ; i ++ ) { sum += a [ i ]; } avg = sum / size ; render avg ; } int principal () { int size , j ; printf ( "Enter the size of array" ); scanf ( "%d" , & size ); bladder b , n [ size ]; for ( j = 0 ; j < size ; j ++ ) { printf ( "Value of due north[%d] : " , j ); scanf ( "%f" , & n [ j ]); } b = average ( due north , size ); printf ( "Average of numbers=%.2f \n " , b ); return 0 ; }
Enter the size of array4
Value of n[0] : 12
Value of northward[1] : 234
Value of n[2] : 12.43
Value of n[3] : 43.43
Average of numbers=75.46
The lawmaking is similar to the previous 1 except that we passed the size of assortment explicitly - float average(float a[], int size).
We can also pass an assortment to a function using pointers. Let's see how.
#include <stdio.h> brandish ( int * p ) { int i ; for ( i = 0 ; i < eight ; ++ i ) { printf ( "n[%d] = %d \n " , i , * p ); p ++ ; } } int main () { int north [ ] = { i , two , 3 , 4 , v , half dozen , 7 , eight }; brandish ( n ); render 0 ; }
n[0] = 1
n[1] = 2
n[ii] = 3
n[3] = 4
n[4] = 5
northward[5] = half-dozen
n[6] = seven
n[vii] = viii
In the above example, the address of the array i.e. address of due north[0] is passed to the formal parameters of the office.
display(int *p) → This means that role 'display' is taking a pointer to an integer.
Now nosotros passed the pointer of an integer i.east. pointer of the array n[] - 'due north' equally per the demand of our office 'display'.
Since 'p' is the address of the array n[] in the function 'brandish' i.e., accost of the first chemical element of the array (n[0]), therefore *p represents the value of north[0]. In the for loop in function, p++ increases the value of p by 1. Then, when i=0, the value of *p gets printed. Then p++ increases *p to *(p+1) and in the second loop, the value of *(p+i) i.e. n[1] too gets printed. This loop continues till i=seven when the value of *(p+7) i.due east. n[7] gets printed.
2D Arrays
What if arrays are 2 dimensional?
Yes, 2-dimensional arrays besides exist and are generally known as matrix. These consist of rows and columns.
Before going into its application, let's start see how to declare and initialize a 2D assortment.
Declaration of 2d Array
Similar to one-dimensional assortment, nosotros ascertain a 2-dimensional assortment as below.
int a[two][4];
Here, 'a' is a 2D array of integers which consists of 2 rows and 4 columns.
It is similar
| Column 0 | Column ane | Cavalcade 2 | Column iii | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Row 0 | a[0][0] | a[0][ane] | a[0][2] | a[0][3] |
| Row 1 | a[i][0] | a[1][one] | a[1][2] | a[1][3] |
Now allow's see how to initialize a ii-dimensional array.
Assigning Values to a two D Array
Same every bit in ane-dimensional assortment, nosotros tin can assign values to the elements of a ii-dimensional array in 2 means too.
In the first method, just assign a value to the elements of the assortment. If no value is assigned to any chemical element, then its value is assumed to be naught.
Suppose nosotros alleged a two-dimensional assortment a[two][2]. Now, we need to assign values to its elements.
int a[ii][2];
a[0][0]=1;
a[0][1]=2;
a[1][0]=3;
a[ane][1]=4;
The 2nd manner is to declare and assign values at the same time as we did in one-dimensional assortment.
int a[two][3] = { one, two, 3, 4, 5, half-dozen };
Here, value of a[0][0] is 1, a[0][1] is 2, a[0][2] is 3, a[one][0] is 4, a[1][ane] is 5 and a[1][2] is 6.
We tin can also write the above code as:
int a[two][3] = {
{1, 2, 3},
{iv, 5, half-dozen }
};
While assigning values to an array at the fourth dimension of proclamation, there is no need to requite size in one dimensional array, but in 2d array, nosotros demand to requite at to the lowest degree the value of the second dimension.
Let's consider different cases of assigning values to an array at the fourth dimension of proclamation.
int a[2][2] = { i, 2, 3, iv }; /* valid */
int a[ ][2] = { 1, 2, iii, 4 }; /* valid */
int a[2][ ] = { 1, two, three, iv }; /* invalid */
int a[ ][ ] = { i, two, 3, 4 }; /* invalid */
Why employ of two D Array
Suppose we take three students each studying 2 subjects (subject 1 and subject ii) and we have to display the marks in both the subjects of the three students. Let's input the marks from the user.
#include <stdio.h> int master () { bladder marks [ 3 ][ 2 ]; int i , j ; for ( i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++ ) { /* input of marks from the user */ printf ( "Enter marks of student %d \north " , ( i + ane ) ); for ( j = 0 ; j < 2 ; j ++ ) { printf ( "Subject field %d \n " , ( j + 1 ) ); scanf ( "%f" , & marks [ i ][ j ]); } } /* printing the marks of students */ for ( i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i ++ ) { printf ( "Marks of student %d \n " , ( i + one ) ); for ( j = 0 ; j < 2 ; j ++ ) { printf ( "Subject field %d : %f \n " , ( j + 1 ), marks [ i ][ j ] ); } } return 0 ; }
Enter marks of pupil one
Subject one
78
Bailiwick 2
67
Enter marks of pupil 2
Subject i
79
Subject 2
87
Enter marks of pupil 3
Discipline one
90
Subject two
89
Marks of student 1
Subject ane : 78.000000
Subject 2 : 67.000000
Marks of educatee two
Discipline 1 : 79.000000
Subject area 2 : 87.000000
Marks of student iii
Subject 1 : 90.000000
Subject area ii : 89.000000
This is something like
| Subject 1 | Subject area two | |
|---|---|---|
| Student one | 78 | 67 |
| Pupil 2 | 79 | 87 |
| Student 3 | 90 | 89 |
To learn from simple videos, you can ever look at our C++ video course on CodesDope Pro. It has over 750 practice questions and over 200 solved examples.
Programming is a skill best acquired by exercise and case rather than from books.
- Alan Turing
merryleespons1954.blogspot.com
Source: https://www.codesdope.com/c-array/
0 Response to "C Programming Read From Keyboard Into Array"
Post a Comment